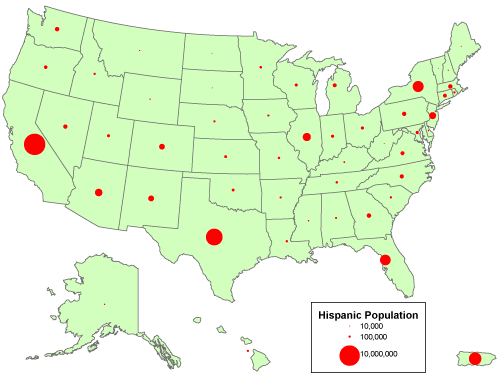
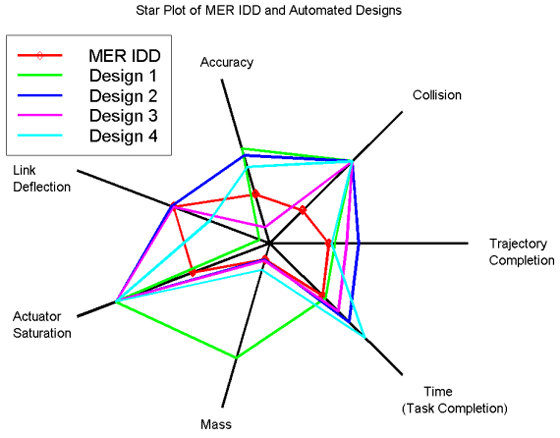
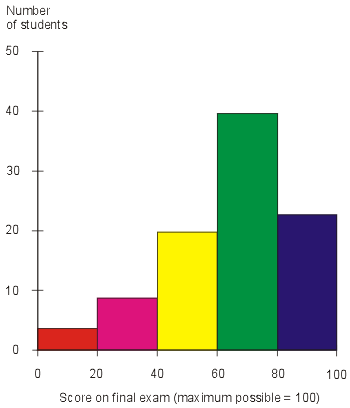
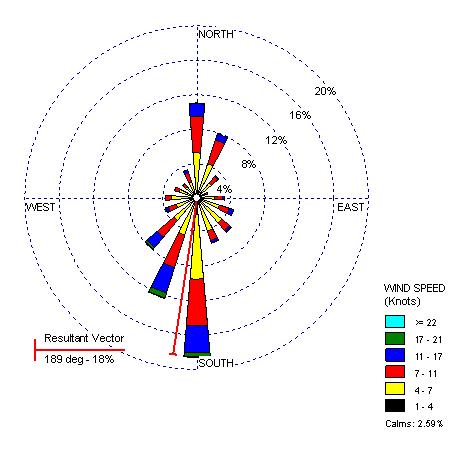
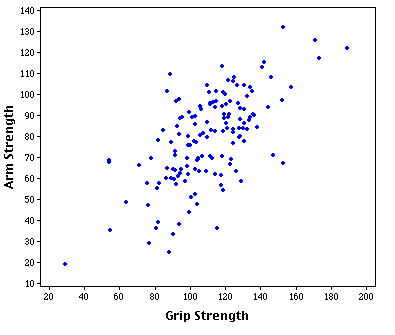
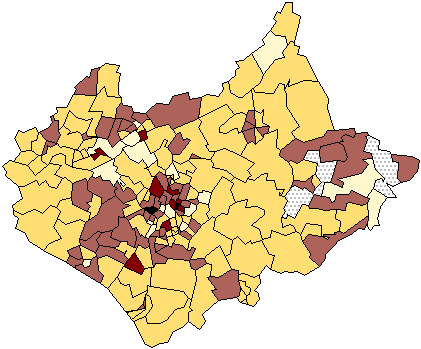
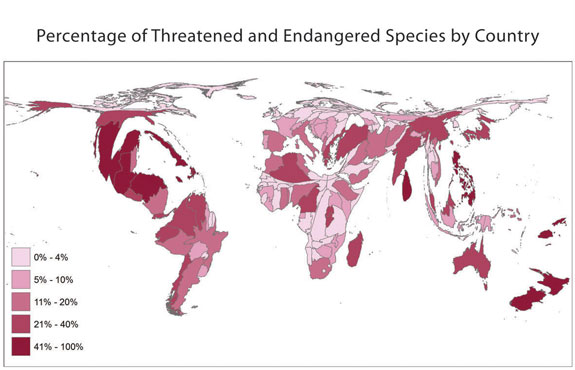
This is an example of a Univariate Choropleth Map. This example illustrates Raw Civil Liberties score. These types are maps are used when objects need to be classified one at a time. These objects may need to be classified individually because when they are put next to something else they have multiple attributes rendering them incomparable.